Modern applications demand agility, elasticity, and resilience, qualities that Kubernetes has made standard for stateless workloads. But what about databases, the inherently stateful core of every application stack?
In our recent webinar, “Running Stateful at Scale: Scalable SQL Databases on Kubernetes,” Michael Wang, Director of Product Management, and Mark Zlamal, Senior Enterprise Architect at Cockroach Labs, explored how CockroachDB bridges the gap between the reliability of traditional SQL databases and the scalability of cloud-native infrastructure.
“CockroachDB gives you the best of both worlds. It combines the consistency and reliability of a traditional database with the scalability and resilience of a cloud-native system.”
– Michael Wang, Director of Product Management, Cockroach Labs
From Fixed Servers to Cloud-Native Systems
For decades, databases like MySQL and PostgreSQL formed the foundation of application development — dependable and ACID-compliant, but designed for an era of fixed servers and manual failovers. When AWS S3 launched in 2006, the era of scalable cloud computing began, quickly followed by NoSQL systems, such as MongoDB, that delivered scale at the expense of transactional integrity. Because of this trade-off, enterprises continued to rely on SQL databases for their transactional integrity and familiar tooling.
Then came the rise of containers and Kubernetes, which revolutionized application scalability and self-healing. However, the database tier lagged behind. Applications were built to scale dynamically while databases stayed static.
Enter Distributed SQL: The Foundation of CockroachDB
Founded in 2015, at the same moment Kubernetes entered the scene, Cockroach Labs set out to design a database purpose-built for the cloud-native world.
CockroachDB is a distributed SQL database. It speaks standard SQL, guarantees full ACID compliance, and scales horizontally without manual sharding or complex routing. Every node is a peer; any node can serve any query whether a read or a write.
As Michael explained:
“CockroachDB automatically shards, replicates, and rebalances data across nodes for efficient utilization and high availability. If a node fails, the system automatically reroutes traffic and heals itself. No manual recovery (or failover) required.”
The result is a database that behaves like a single logical system, even when it’s distributed across regions, clouds, or continents.
Why Kubernetes and CockroachDB Fit Naturally Together
Mark Zlamal took the virtual stage to show how CockroachDB and Kubernetes align perfectly in design philosophy: resiliency, scalability, and self-healing.
Scalability: Both systems scale horizontally: Kubernetes adds nodes, CockroachDB balances data across them.
Resilience: If a Kubernetes worker node fails, CockroachDB rebalances its replicas automatically to maintain availability.
Consistency: CockroachDB ensures serializable isolation across nodes, maintaining strong consistency even as the cluster scales or different kinds of failures occur.
Mark demonstrated a live cluster scaling from three to five nodes, under load, in minutes. Without downtime, CockroachDB redistributed data automatically and increased throughput by up to 30%. As he noted, “You can perform real-time schema and infrastructure changes on a running system. That’s the power of distributed SQL.”
RELATED
Hear from Jack Chi, Senior Software Engineer at Iterable, on "How Iterable Deploys 4 Use Cases on CockroachDB and Kubernetes":
Built for Cloud-Native Freedom
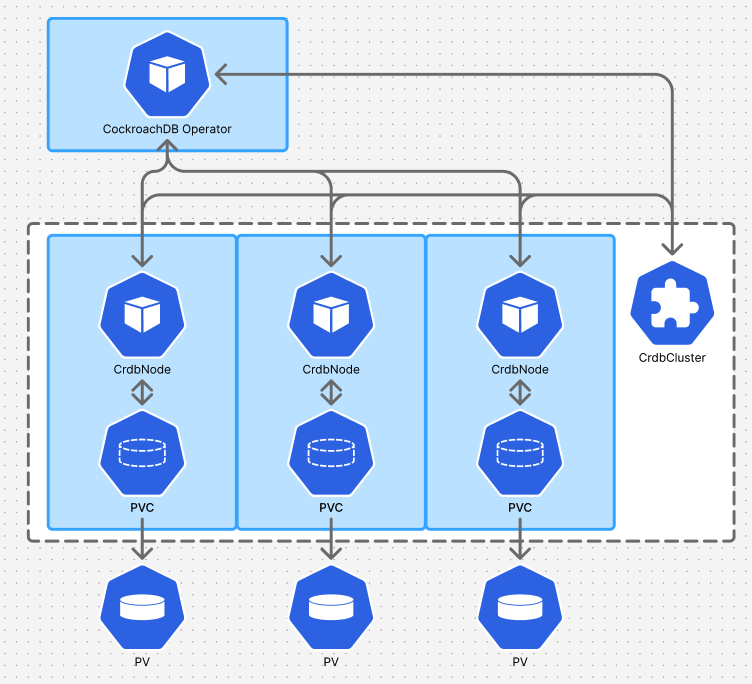
Architecture diagram of the CockroachDB Operator on Kubernetes.
CockroachDB can be deployed anywhere: on-prem, across clouds, or in hybrid architectures. It supports Helm, YAML manifests, and a Kubernetes Operator (the same operator Cockroach Labs uses internally to power CockroachDB Cloud). This consistency allows teams to automate deployments, integrate CI/CD pipelines, and replicate their environments across clusters with confidence.
“Whether you’re running OpenShift, EKS, or GKE,” Mark explained, “CockroachDB’s architecture aligns perfectly with Kubernetes’ core principles.”
Q&A Highlights
Does CockroachDB make the CAP theorem obsolete? Not exactly, but it makes the A (availability) tunable. CockroachDB is a CP system, guaranteeing consistency and partition tolerance, while giving users control over availability depending on their topology.
How does it handle spot instance failures? CockroachDB relies on persistent disks (like AWS EBS) to preserve state. If instances fail, data can be reattached and recovered automatically.
Is Kubernetes ready for stateful workloads? Yes. With StatefulSets, persistent volumes, and operators, Kubernetes now supports running databases effectively. But CockroachDB stands apart because it was designed for this model from day one, not retrofitted into it.
Final Thoughts
At its core, CockroachDB was designed to run like any other cloud-native workload: seamlessly, elastically, and reliably. It turns the idea of “stateful” on its head, enabling true distributed performance and auto-healing resilience.
“We built CockroachDB at the intersection of databases and Kubernetes. It scales and heals like your stateless services, but with the full power and guarantees of SQL.”
– Michael Wang, Director of Product Management, Cockroach Labs
Watch the Webinar On-Demand
Want to see how it works in action? Watch the webinar on-demand and get $400 in free CockroachDB Cloud credits to try it yourself.